This will be a basic example on using a python Lambda function to check S3 Buckets.
Table of Contents
Create a Lambda Function in AWS
Once you are signed into your AWS Account, navigate to the Lambda > Functions and create a function
In the creation screen, we don’t really need to change much other than giving our function a name. In this case I am creating a Lambda function to check the S3 buckets so I am going with “S3BucketCheck”
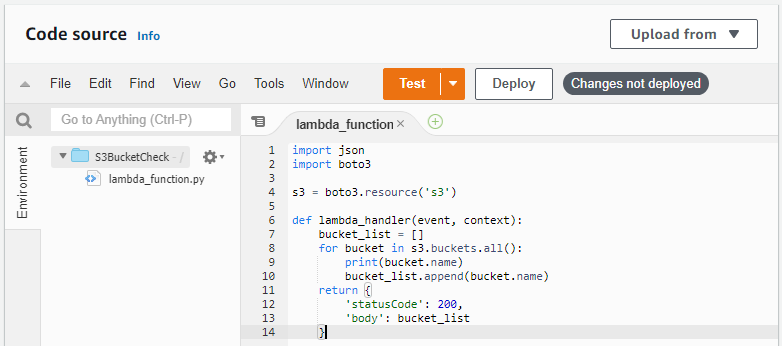
Python Code Source for Function
Now that we have the Lambda function created in our AWS account, it’s time to configure it to perform what actions we want it take with our python code.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
import json
import boto3
s3 = boto3.resource('s3')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
bucket_list = []
for bucket in s3.buckets.all():
print(bucket.name)
bucket_list.append(bucket.name)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': bucket_list
}
Explaining the Code Source
The Amazon python SDK is called boto3 and readily available for you to use in the Lambda development environment so there is no need to install anything. Simply “import boto3”
Next we setup the service object that we are going to be interfacing with. This is done by calling boto3 and then specifying resource and then calling what resource we want to interact with. ('s3') in this case
Next we set up the Lambda Function itself by starting with a function using def. We will use lambda_handler as a convention and pass an event and context.
In the function, we will create an emtpy list named bucket_list that will later contain the names of the s3 buckets this function will go fetch for us.
We are going to use a for loop to iterate through the s3 bucket object for all buckets and then print those names using bucket.name as we add them to our empty list using append.
Finally we can create a return status from the results of the function. Here we want a status code and to give us the list it created from what was found in our S3 Buckets list of our AWS account.
Deploy your changes!
Test Event
We have created a function in AWS, and filled in our code source using python. Now moving onto the test event.
Configure
To configure, we will first give our test event a name. For this example I am using “S3List”. We can leave the Event JSON as default key values and click “Save”. 
Troubleshoot and Resolve
If we run our test as it is you will an error occured (AccessDenied) when calling the ListBuckets operation: Access Denied.
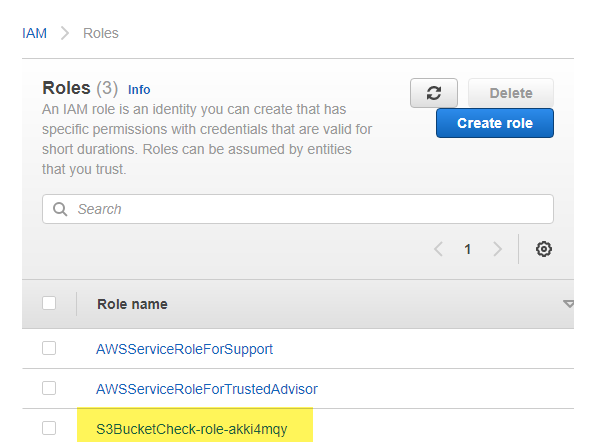
To resolve this we will need to give our lambda function’s role in AWS the proper permissions to interact with the S3 buckets. Head over to IAM > Roles and you will see your auto generated lambda role from when you first created the lambda function in AWS.
Warning: I’m going to be giving my lambda function full S3 access for the sake of this example. There are best practices out there that should be followed for proper permissions for something such as this. Please read AWS Lambda Permissions here
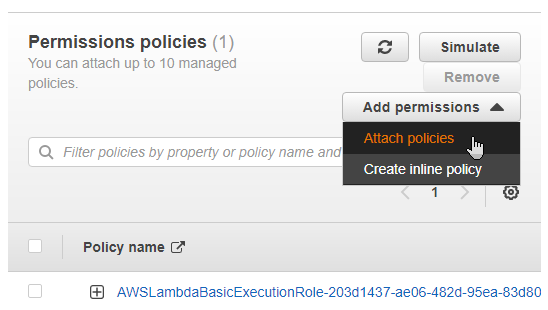
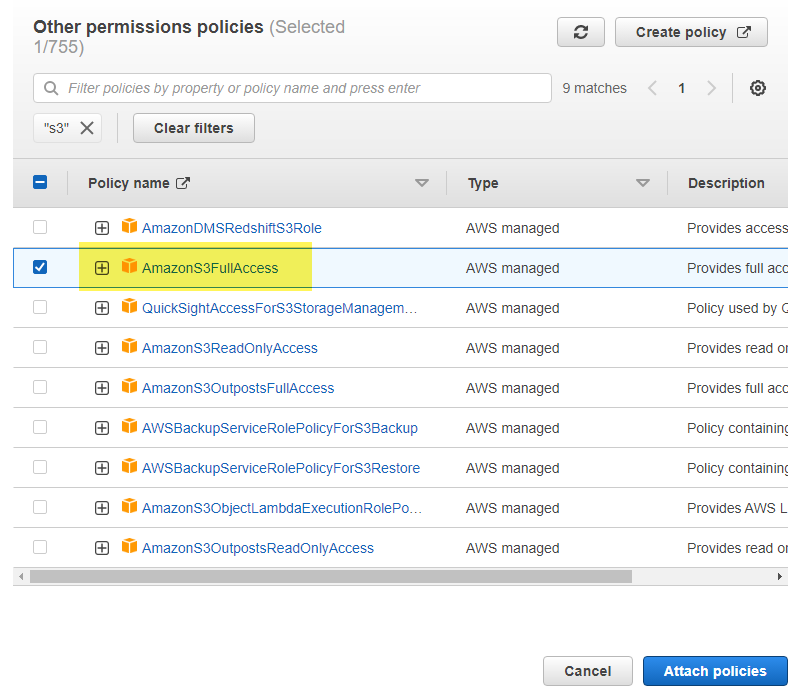
Open the lambda role and “Add Permissions” then “Attach Policies”
Filter for “S3” and check the box to choose the AmazonS3FullAccess policy and then click Attach Policies.
Now we have two policies on our lambda function role and we can check that we have added the correct permissions here.
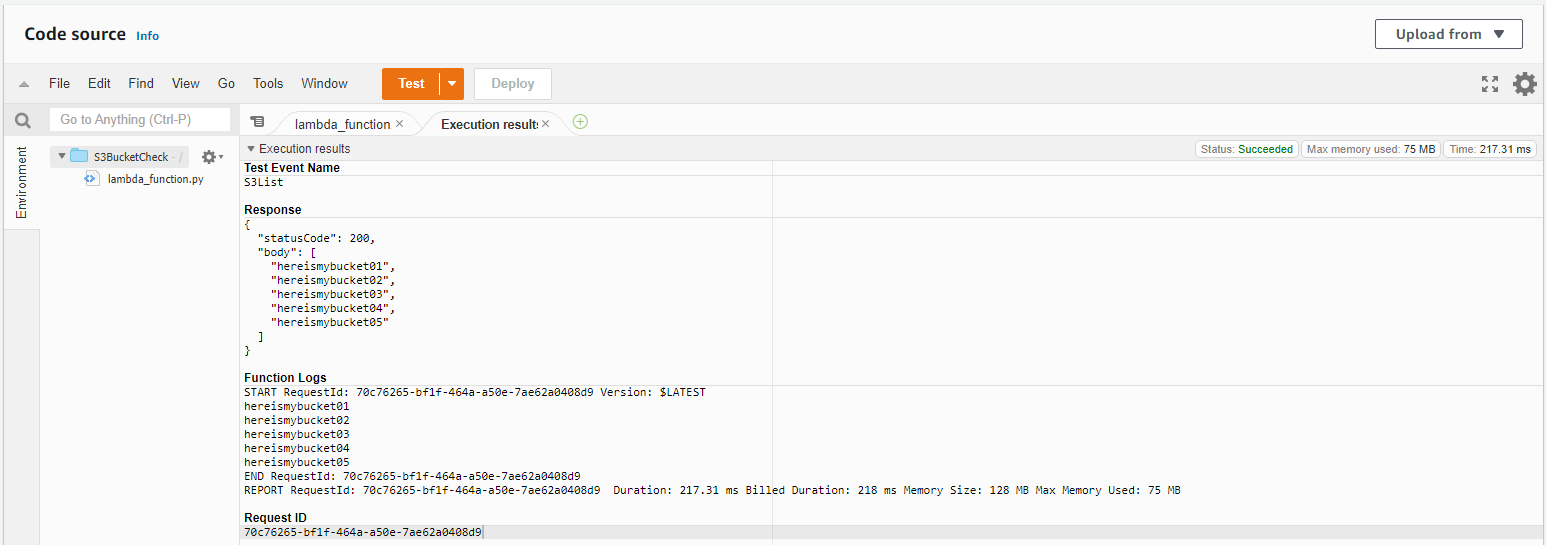
As we can see, if we re-run our test will are getting the list of names for the S3 Buckets that I created earlier for this test.
Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Test Event Name
S3List
Response
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": [
"hereismybucket01",
"hereismybucket02",
"hereismybucket03",
"hereismybucket04",
"hereismybucket05"
]
}
Function Logs
START RequestId: 70c76265-bf1f-464a-a50e-7ae62a0408d9 Version: $LATEST
hereismybucket01
hereismybucket02
hereismybucket03
hereismybucket04
hereismybucket05
END RequestId: 70c76265-bf1f-464a-a50e-7ae62a0408d9
REPORT RequestId: 70c76265-bf1f-464a-a50e-7ae62a0408d9 Duration: 217.31 ms Billed Duration: 218 ms Memory Size: 128 MB Max Memory Used: 75 MB
Request ID
70c76265-bf1f-464a-a50e-7ae62a0408d9
And with this, we can see we were able to successfully pull a list of our S3 Buckets using a Python Lambda function.
Future Thoughts
While this is a simply a dip of the toe in the waters of AWS Lambda, I have ideas to dig deeper into this topic by something along the lines of using ACM to send events via Cloudwatch and using a lambda function to handle the renewal. For example, add the magic DNS entry to the DNS of choice (if Route 53 is not being used) and then retrieve the cert and scp it to the ec2 instance.