Proxmox VE is an open-source server platform for enterprise virtualization. As a Debian-based Linux distribution, Proxmox uses a modified Ubuntu kernel to run multiple virtual machines and containers on a single server.
Table of Contents
- Download Proxmox ISO Image
- Prepare Installation Medium
- Launch the Proxmox Installer
- Run Proxmox
- Removing Subscription Pop-Up on Log-In
- Create a VM
- Configure Proxmox Virtual Environment
- (Bonus) Enable Dark Mode!!!
Download Proxmox ISO Image
The first step is to download the Proxmox VE ISO image.
Navigate to the official Proxmox Downloads page and select Proxmox Virtual Environment.
This takes you to the Proxmox Virtual Environment Archive that stores ISO images and official documentation. Select ISO Images to continue.
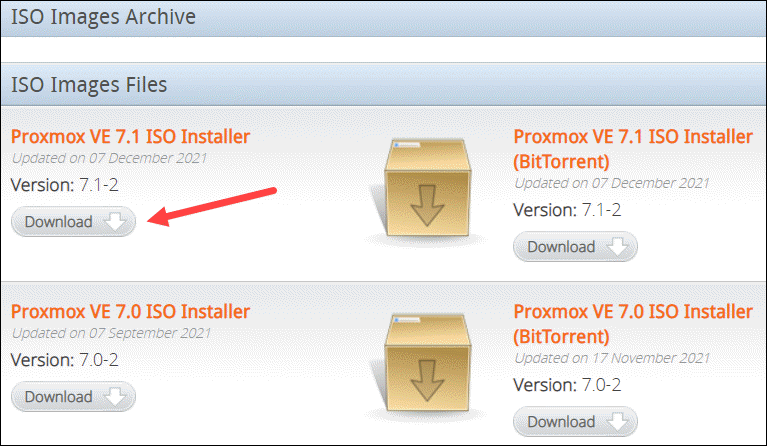
At the time of writing, the latest version of the Proxmox VE ISO Installer is 7.1. If a newer version is available, it is listed at the top. Click Download and save the file.
Prepare Installation Medium
Copy the Proxmox ISO image on a CD/DVD or a USB flash drive. Although both options are possible, it is assumed that most systems won’t have an optical drive.
Plug in the USB drive and copy the ISO image to the USB stick using the command line or a USB formatting utility (such as Etcher or Rufus).
If you are working on Linux, the fastest way is to create a bootable USB is to run the command:
1
dd bs=1M conv=fdatasync if=./proxmox-ve_*.iso of=/device/nameCopied!
If needed, modify the file name and path in if=./proxmox-ve_*.iso and make sure to provide the correct USB device name in of=/device/name.
To find the name of your USB stick, run the following command before and after plugging in the device:
1
lsblk
Compare the output. The additional entry in the second output is the name of the device.
Launch the Proxmox Installer
Move to the server (machine) where you want to install Proxmox and plug in the USB device.
While the server is booting up, access the boot menu by pressing the required keyboard key(s). Most commonly, they are either Esc, F2, F10, F11, or F12.
Select the installation medium with the Proxmox ISO image and boot from it.
Next, the Proxmox VE menu appears. Select Install Proxmox VE to start the standard installation.
Read and accept the EULA to continue.
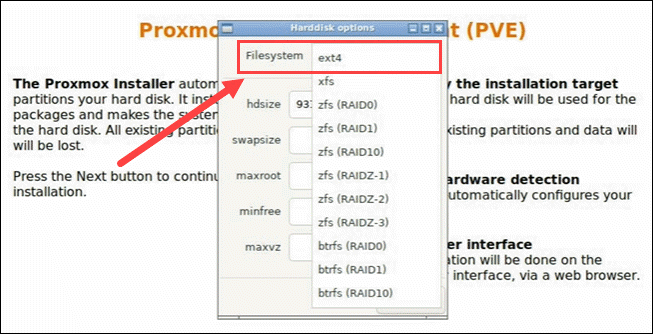
Choose the target hard disk where you want to install Proxmox. Click Options to specify additional parameters, such as the filesystem. By default, it is set to ext4.
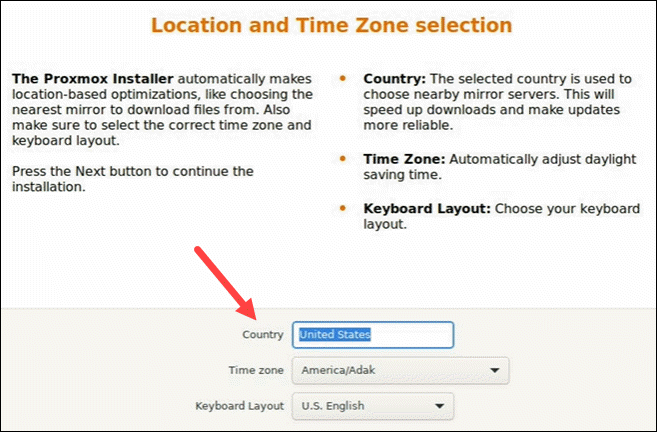
Then, set the location, time zone, and keyboard layout. The installer autodetects most of these configurations.
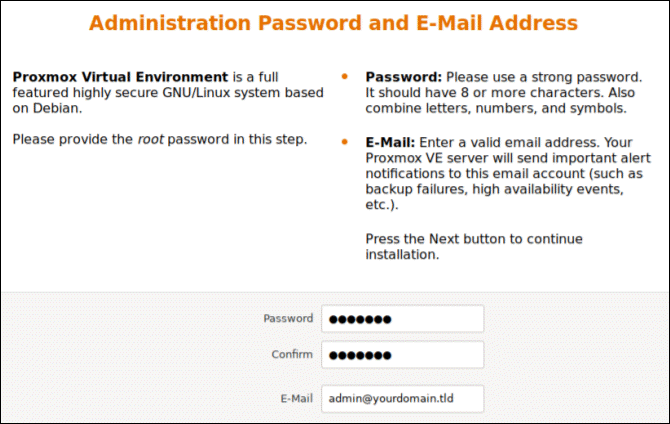
Create a strong password for your admin credentials, retype the password to confirm, and type in an email address for system administrator notifications.
The final step in installing Proxmox is setting up the network configuration. Select the management interface, a hostname for the server, an available IP address, the default gateway, and a DNS server. During the installation process, use either an IPv4 or IPv6 address. To use both, modify the configuration after installing.
The installer summarizes the selected options. After confirming everything is in order, press Install.
After the installation is complete, remove the USB drive and reboot the system.
Run Proxmox
Once the installation is completed and the system rebooted itself, the Proxmox GRUB menu loads. Select Proxmox Virtual Environment GNU/Linux and press Enter.
Next, the Proxmox VE welcome message appears. It includes an IP address which loads Proxmox. Navigate to that IP address in a web browser of your choice.
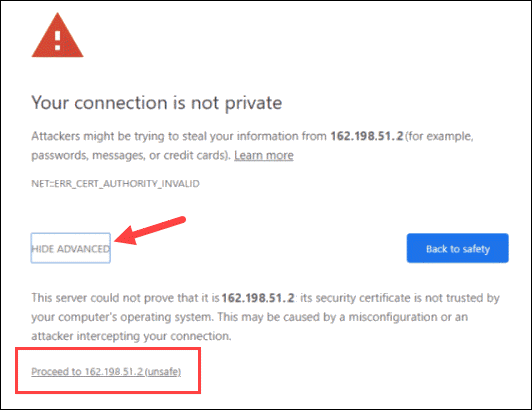
After navigating to the required IP address, you will most likely see a warning message that the page is unsafe because Proxmox VE uses self-signed SSL certificates. Select to proceed to the Proxmox web management interface.
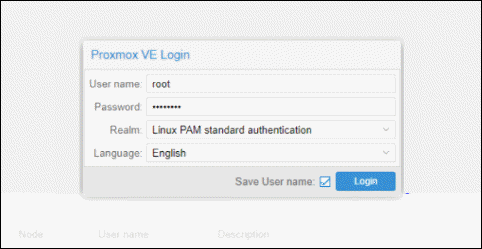
To access the interface, log in as root and provide the password set when installing Proxmox.
A dialogue box pops up saying there is no valid subscription for the server. Proxmox offers an add-on service you can subscribe to, which is optional. To ignore the message, click OK.
Removing Subscription Pop-Up on Log-In
One-Line Command
Run this command in the terminal of the host machine running your ProxMox instance.
1
sed -Ezi.bak "s/(Ext.Msg.show\(\{\s+title: gettext\('No valid sub)/void\(\{ \/\/\1/g" /usr/share/javascript/proxmox-widget-toolkit/proxmoxlib.js && systemctl restart pveproxy.service
Manual Commands
Below is the manual process of acheiving the same results as the command above in multi-command steps.
Change to working directory
1
cd /usr/share/javascript/proxmox-widget-toolkit
Make a backup
1
cp proxmoxlib.js proxmoxlib.js.bak
Edit the file
1
nano proxmoxlib.js
Locate the following code (Use ctrl+w in nano and search for “No valid subscription”)
1
2
Ext.Msg.show({
title: gettext('No valid subscription'),
Replace “Ext.Msg.show” with “void”
1
2
void({ //Ext.Msg.show({
title: gettext('No valid subscription'),
Restart the Proxmox web service (also be sure to clear your browser cache, depending on the browser you may need to open a new tab or restart the browser)
1
systemctl restart pveproxy.service
You can quickly check if the change has been made:
1
grep -n -B 1 'No valid sub' proxmoxlib.js
You have three options to revert the changes:
- Manually edit proxmoxlib.js to undo the changes you made
- Restore the backup file you created from the proxmox-widget-toolkit directory:
mv proxmoxlib.js.bak proxmoxlib.js - Reinstall the proxmox-widget-toolkit package from the repository:
apt-get install --reinstall proxmox-widget-toolkit
Create a VM
Now that you logged in to the Proxmox web console, create a virtual machine.
Before going through the steps to create a virtual machine, make sure you have ISO images for installation mediums. Move to the resource tree on the left side of your GUI.
Select the server you are running and click on local (pve1). Select ISO Images from the menu and choose between uploading an image or downloading it from a URL.
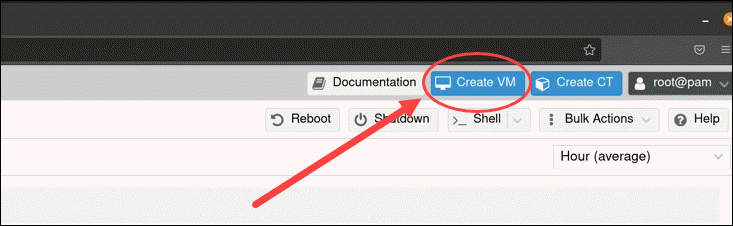
Once you have added an ISO image, move on to spinning up a virtual machine. Click the Create VM button located on the right side of the header in the GUI.
Provide general information about the VM:
Start by selecting the Node. If you are starting and have no nodes yet, Proxmox automatically selects node 1 (pve1). Provide a VM ID. Each resource has to have a unique ID. Finally, create a name for the VM. Use an easily identifiable name.
Next, switch to the OS tab and select the ISO image you want for your VM. Define the Type of the OS and kernel Version. Click Next to continue.
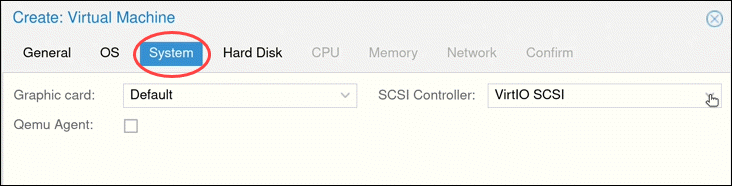
Modify system options (such as the Graphic card and SCSI controller) or leave the default settings.
Then, configure any Hard Disk options you want the VM to have. Generally, you can leave all the default settings. However, if the physical server is using an SSD, enable the Discard option.
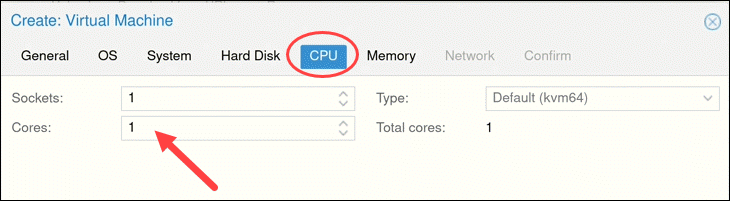
The number of Cores the physical server has determines how many cores you can provide to the VM. The number of cores allocated also depends on the predicted workload.
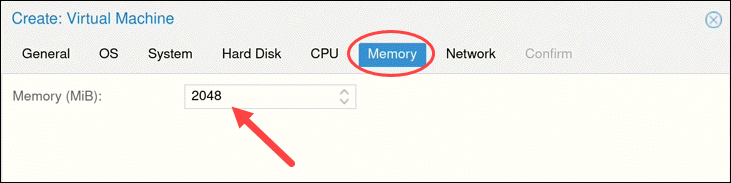
Next, choose how much Memory (MiB) you want to assign to the VM.
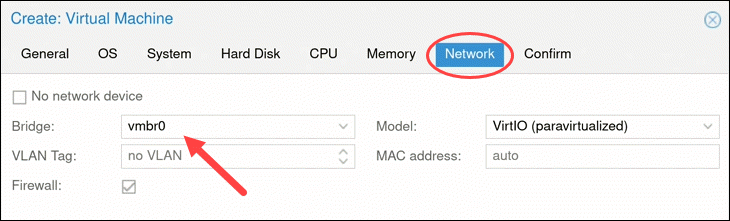
Move on to the Network tab. It is recommended to separate the management interface and the VM network. For now, leave the default setting.
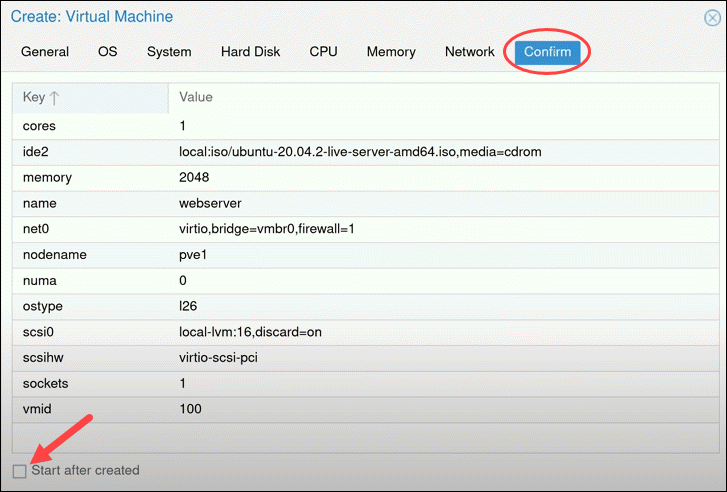
After clicking Next, Proxmox loads the Confirm tab that summarizes the selected VM options. To start the VM immediately, check the box under the listed information or start the VM manually later. Click Finish to create the VM.
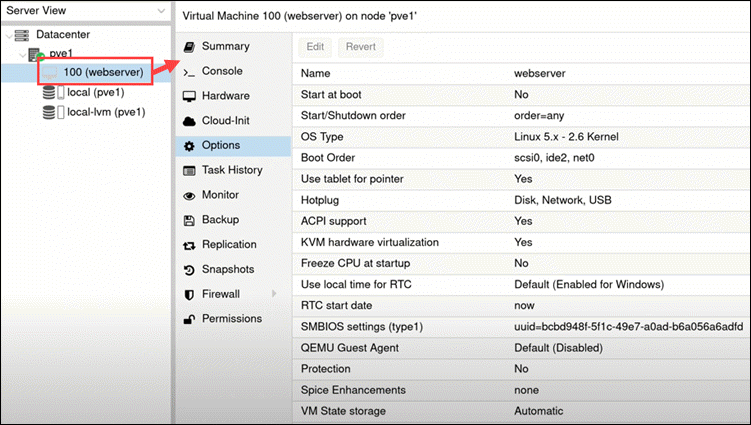
See the newly created VM in the resource tree on the left side of the screen. Click on the VM to see its specifications and options.
Configure Proxmox Virtual Environment
After creating a virtual machine, move on to configuring the environment.
Start the VM at Boot
If the Start at boot option is set to No, the VM does not automatically start after rebooting the server. This means you need to log in to the Proxmox interface and start the VM manually.
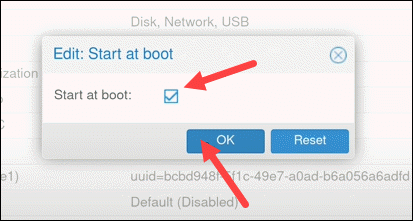
To change the default setting, highlight the option and click the Edit button above.
Check the box and click OK.
Increase/Decrease Virtual Disk Size
The simplest way to increase or decrease the virtual disk size of a VM is through the command line interface, which can be done online or offline.
When increasing disk space, modify the partition table and file system inside the VM to update to the new size.
When decreasing a VM’s disk space, make sure to back up any data you want to save and reduce the file system and partition inside the VM first.
The main syntax for increasing/decreasing virtual disk size is:
1
qm resize [virtual_machine_ID] [disk] [size]Copied!
For instance, to add 10G to a virtio0 disk on a VM with the ID 100, run:
1
qm resize 100 virtio0 +10G
Enable NAT Networking Mode
As mentioned above, it’s a good idea to change the default bridge networking mode to prevent the Proxmox host and VMs being on the same network. To create a separate network, enable NAT networking mode.
To do so, edit the Interfaces file. Open the command line and run:
1
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces
The file shows that vmbr0 is the default bridge network for Proxmox, as in the lines below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
iface eno1 inet manual
auto vmbr0
iface vmbr0 inet static
address 10.10.22.215
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 10.10.22.1
bridge_ports eno1
bridge_stp off
bridge_fd 0
Add the following content to the file:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
auto vmbr1
iface vmbr1 inet static
address 10.10.10.1
netmask 255.255.255.0
bridge_ports none
bridge_stp off
bridge_fd 0
post-up echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
post-up iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s '10.10.10.0/24' -o vmbr0 -j MASQUERADE
post-down iptables -t nat -D POSTROUTING -s '10.10.10.0/24' -o vmbr0 -j MASQUERADE
Save and exit.
Finally, bring up the the new interface with:
1
sudo ifup vmbr1
Next time you create a VM, vmbr0 and vmbr1 will be available for the bridge network option. Select vmbr1 to keep the VM on a separate network from Proxmox.
(Bonus) Enable Dark Mode!!!
Everything is dark, including the graphs, context menus and all in between! Eyes need not be fried.
Install
The installation is done via the CLI utility. Run the following commands on the PVE node serving the Web UI:
1
2
~# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Weilbyte/PVEDiscordDark/master/PVEDiscordDark.sh
~# bash PVEDiscordDark.sh install
Or this oneliner
1
bash <(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Weilbyte/PVEDiscordDark/master/PVEDiscordDark.sh ) install
Uninstall
To uninstall the theme, simply run the utility with the uninstall command.